Microsoft Sentinel: The Ultimate Tool for Cloud Security Monitoring and Protection
Hello everyone! Welcome back from ARTIFICALAB LTD! Today, we will explore about the Microsoft Sentinel, which is a cloud-native security information and event management (SIEM) solution.
The best part of SIEM tool is that it is solely designed to provide comprehensive security monitoring and protection for the Azure Cloud Platform. This article will discuss into how Microsoft Sentinel stands out as the ultimate tool for cloud security, with real-world examples to illustrate its effectiveness.

Introduction to Microsoft Sentinel
Microsoft Sentinel is a scalable, cloud-native SIEM and security orchestration automated response (SOAR) solution. It leverages the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to deliver intelligent security analytics and threat intelligence across the enterprise. Sentinel is designed to help organizations detect, investigate, and respond to security threats in real-time, making it an essential tool for modern cloud security.

Figure: Microsoft Sentinel, Image courtesy of Microsoft Azure
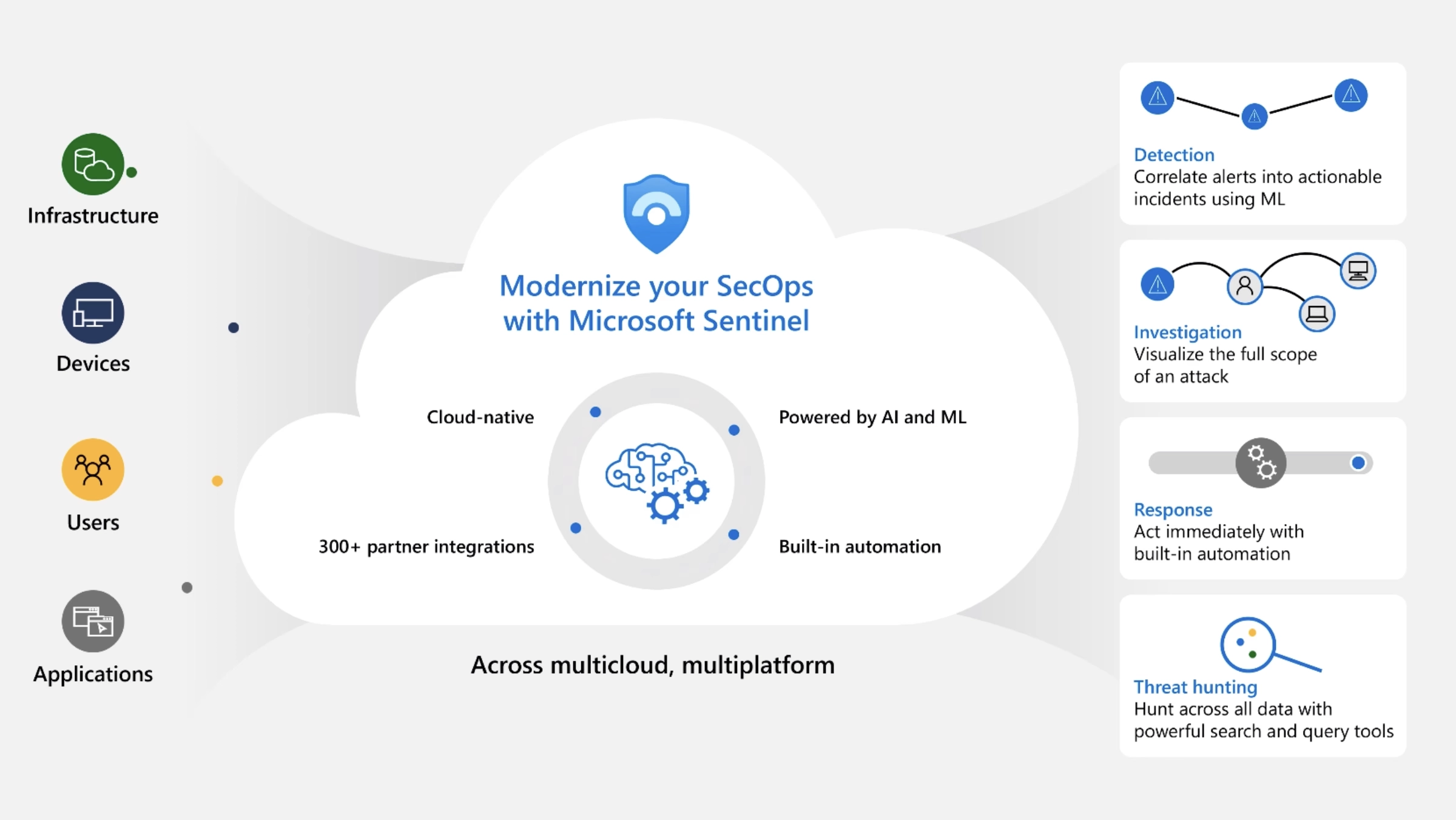
Figure: Microsoft Sentinel: Detection, Investigation, Response, & Threat Hunting, Image courtesy of Microsoft Azure
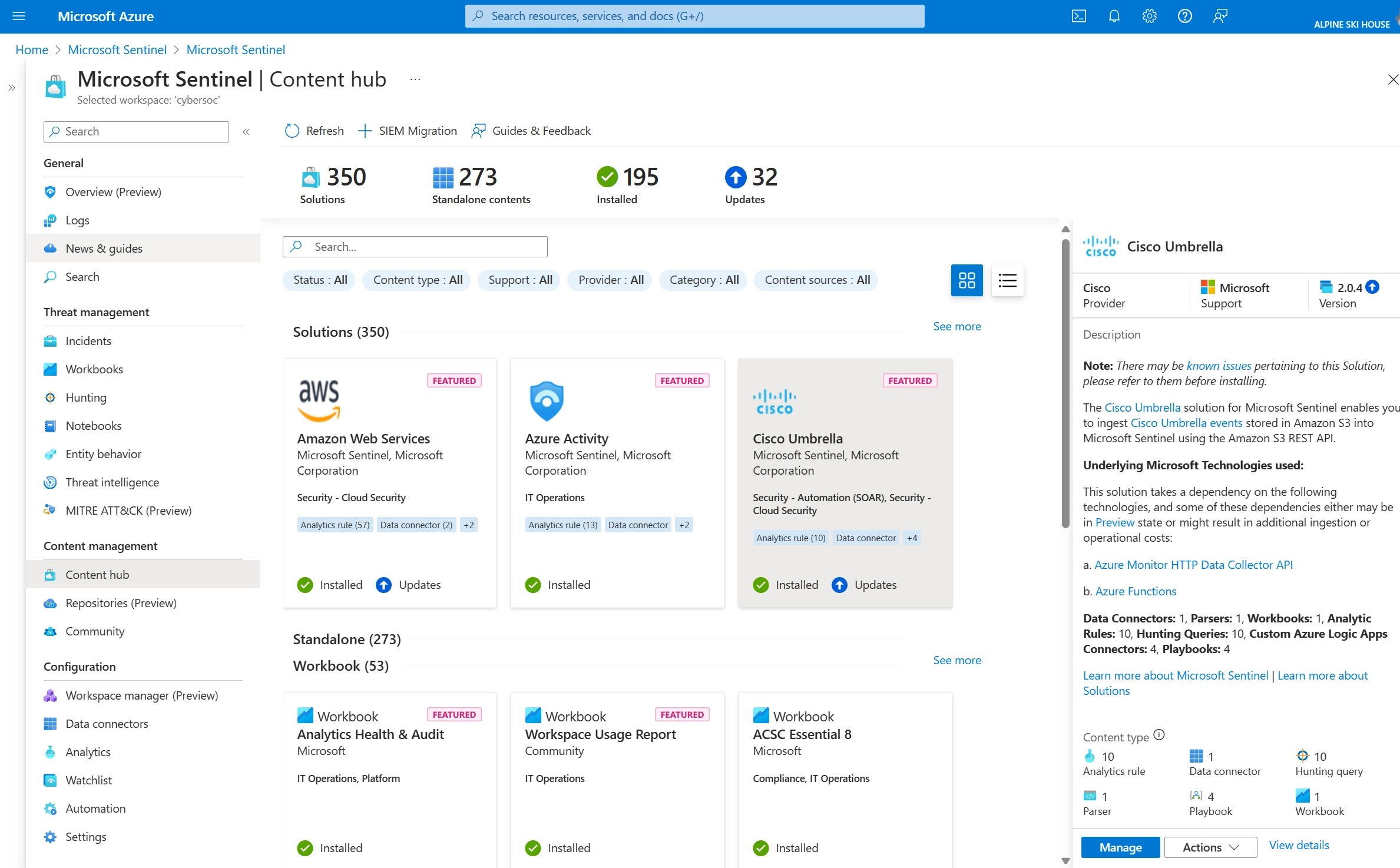
Figure: Microsoft Sentinel in Azure Cloud, Image courtesy of Microsoft Azure
Four main key responsibilities of Microsoft Sentinel
With Microsoft Sentinel, we as Cloud Engineers can now perform securing our client systems' end-to-end security operations including collection, detection, investigation, and response:
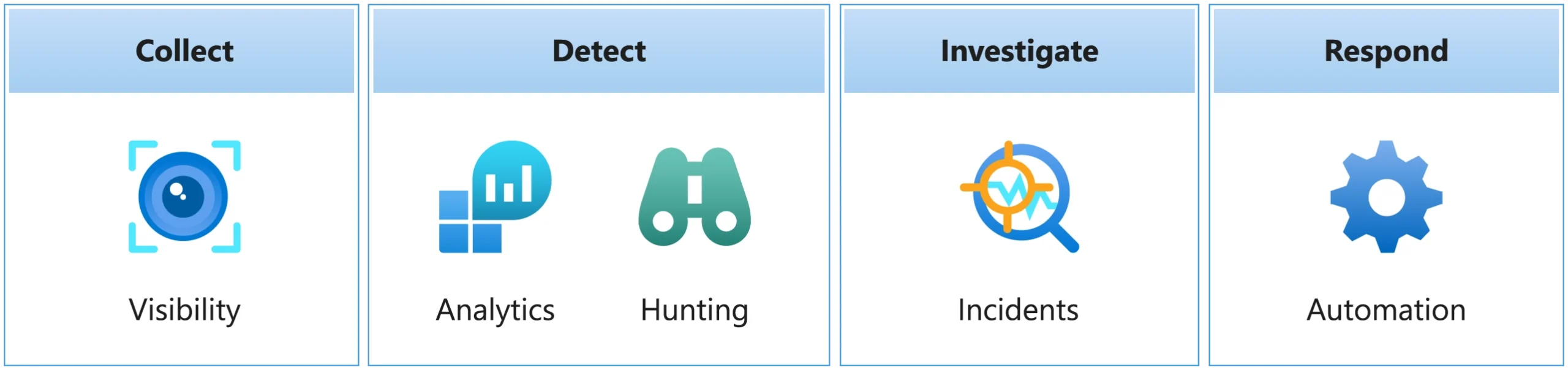
Figure: End-to-end security in Microsoft Sentinel, Image courtesy of Microsoft Azure
How Microsoft Sentinel Works
As we now understood that Microsoft Sentinel protects our Azure Cloud Systems in end-to-end ways, thus it is now essential to understand the key components of Microsoft Sentinel and how it works!
The first one starts with Data Connectors!
Data connectors in Microsoft Sentinel
The very first thing we need to prepare in Microsoft Sentinel is how to ingest the required data (such as logs) into the Microsoft Sentinel. This is because without data, Sentinel cannot analyze anything, identify threats and protects us before it's too late!
For that, Data Connectors in Microsoft Sentinel can help us with that. The data sources it can ingest include not limited to:
- syslog
- Common Event Format (CEF)
- Trusted Automated eXchange of Indicator Information (TAXII) (for threat intelligence)
- Azure
- AWS services
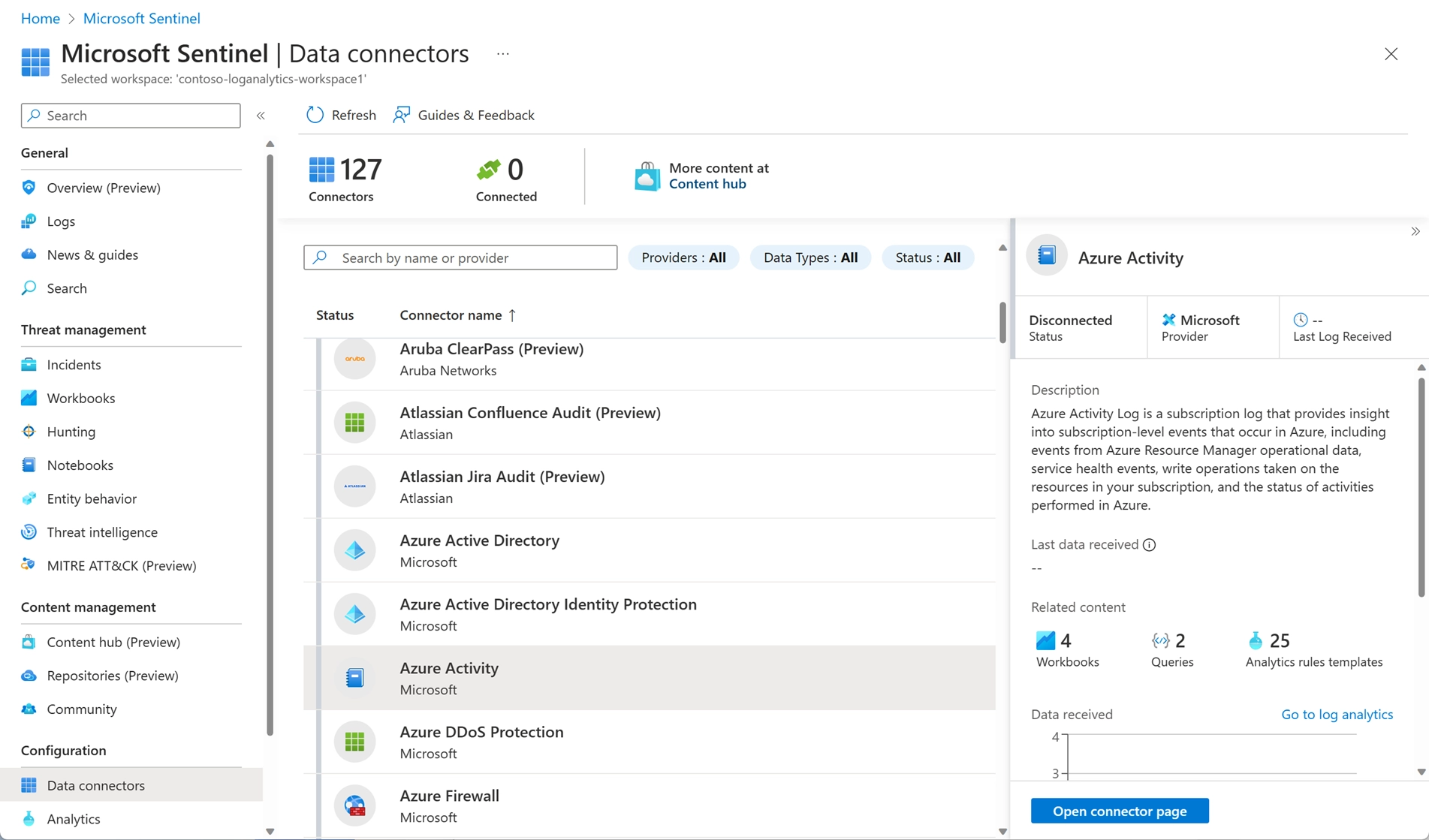
Figure: Data Connectors in Microsoft Sentinel, Image courtesy of Microsoft Azure
Log retention in Microsoft Sentinel
Then, after Data Connectors have ingest the required data sources into the Sentinel, the next thing we need to configure is how to and where to store these logs.
For that, according to Microsoft, these logs will be stored in the Azure Log Analytics Feature. Within this Log Analytics, we can use the Kusto Query Language (KQL) to query the required data. In fact, please keep in mind that KQL is a rich query language that gives you the power to dive into and gain insights from our data.
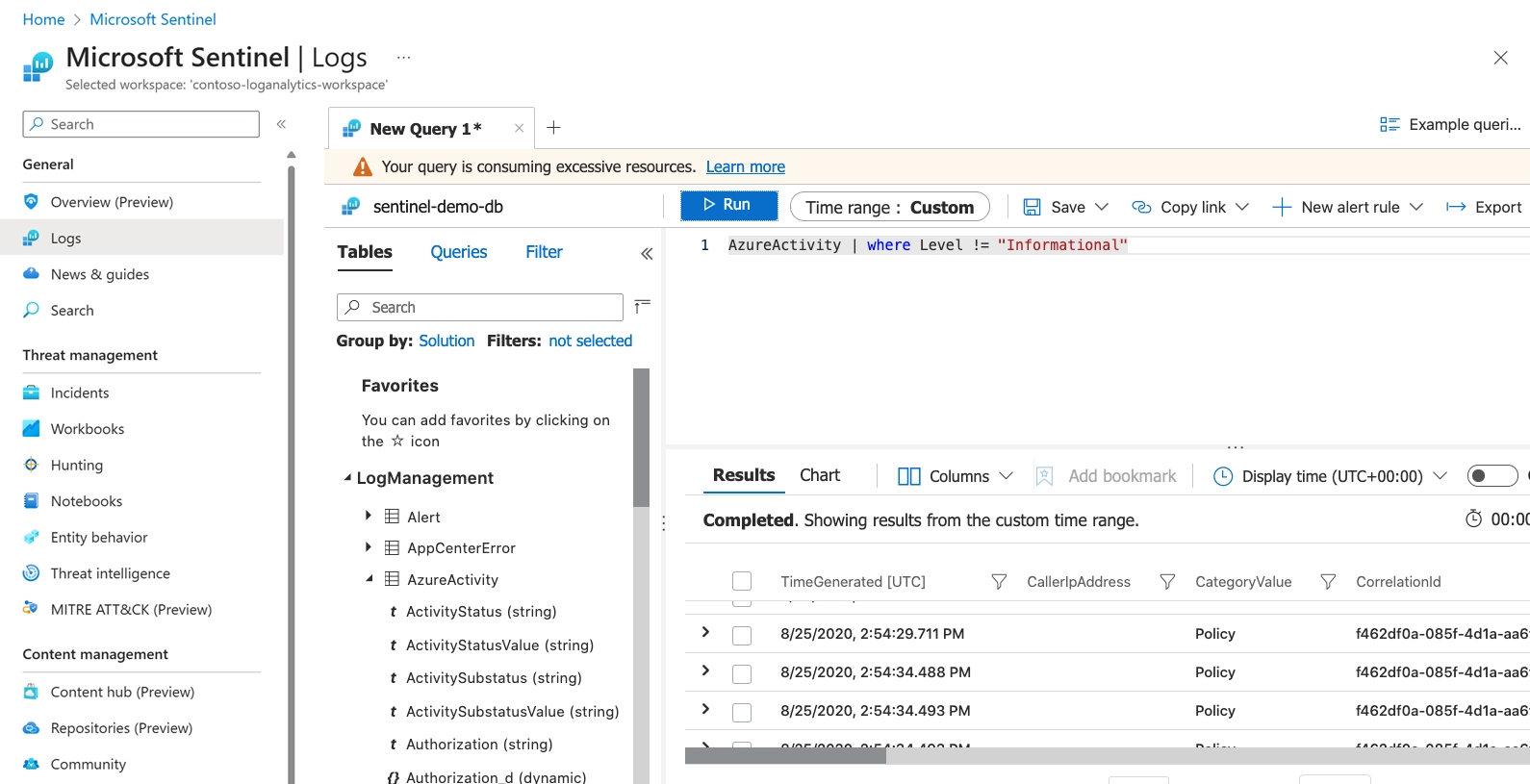
Figure: Log Analytics in Microsoft Sentinel, Image courtesy of Microsoft Azure
Workbooks in Microsoft Sentinel
Then, to analyze the current threats situation, we need Workbooks! Indeed, workbooks are essentially dashboards (as shown figure below), in which the insights can be extracted by using KQL query on the underlying data.
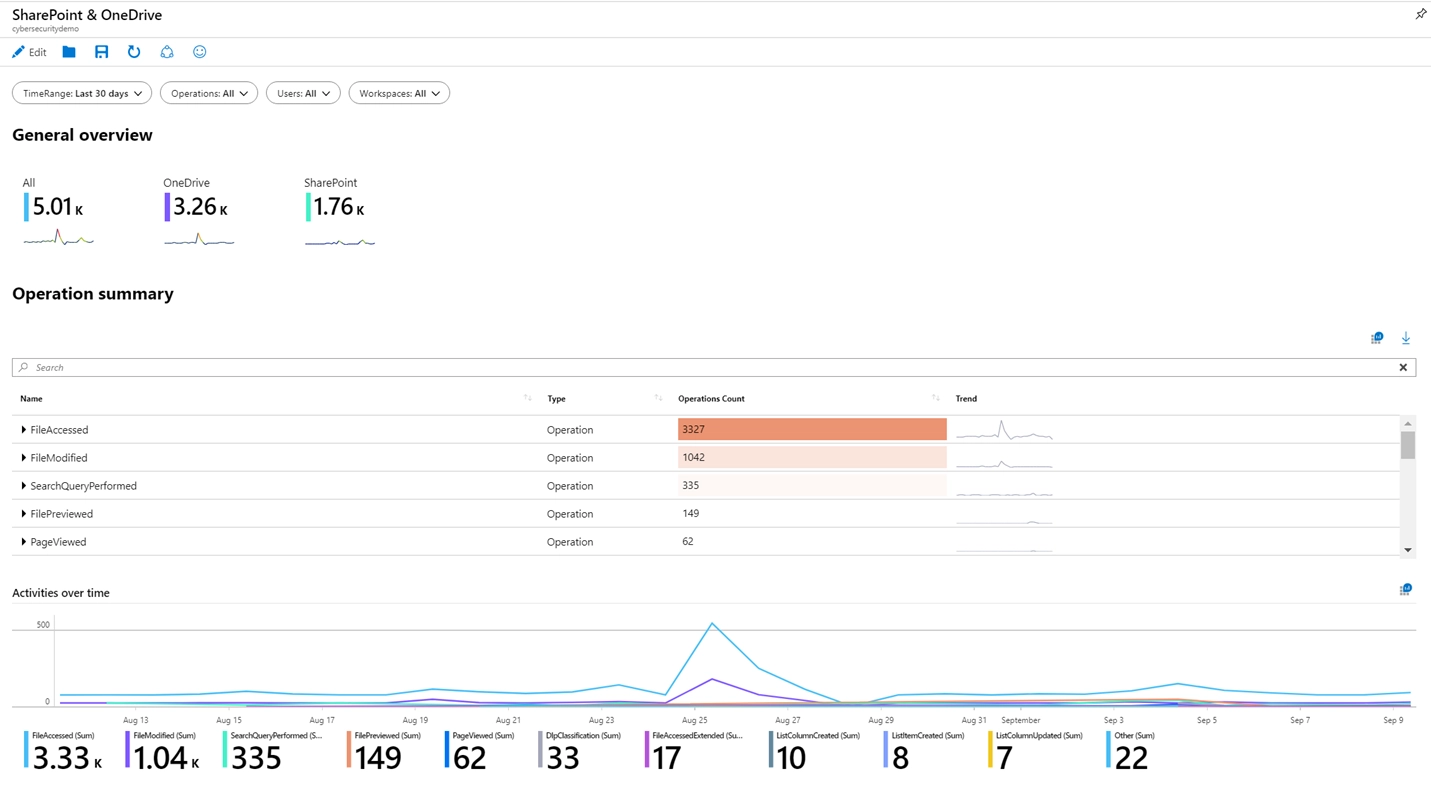
Figure: Workbooks in Microsoft Sentinel, Image courtesy of Microsoft Azure
Analytics Alerts in Microsoft Sentinel
For proactive analytics such as anomaly detection and detecting any suspicious events based on your data sources, this Analytics Alerts feature will help Cloud Engineers in Microsoft Sentinel. Various types of alerts are possible and some include built on machine-learning models that are proprietary to Microsoft. It's better to try them!
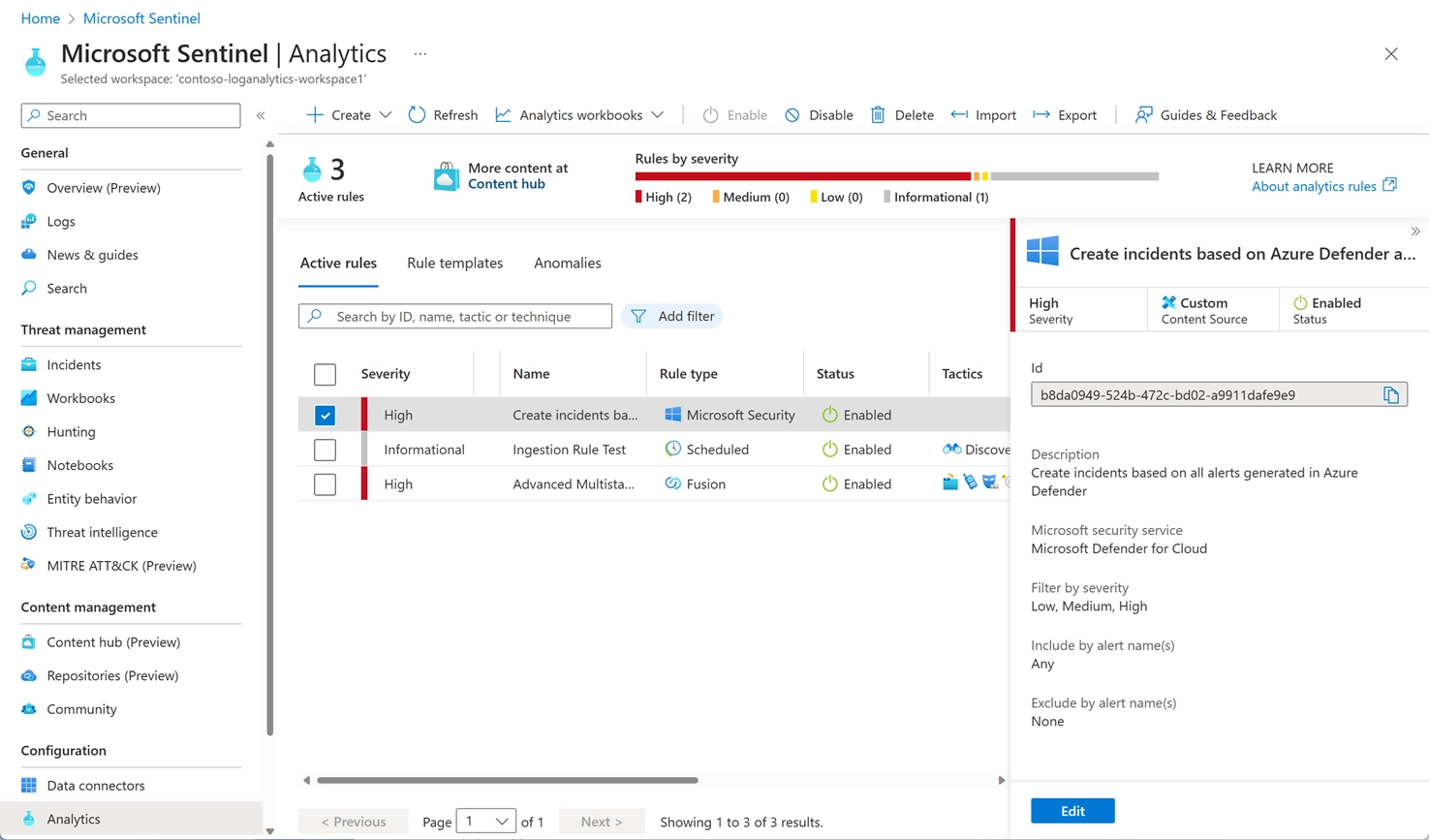
Figure: Analytics Alerts in Microsoft Sentinel, Image courtesy of Microsoft Azure
Threat Hunting in Microsoft Sentinel
The next one feature in Microsoft Sentinel is the threat hunting feature. Using common built-in hunting queries, Cloud Security Engineers can quickly identify which types of threats currently facing.
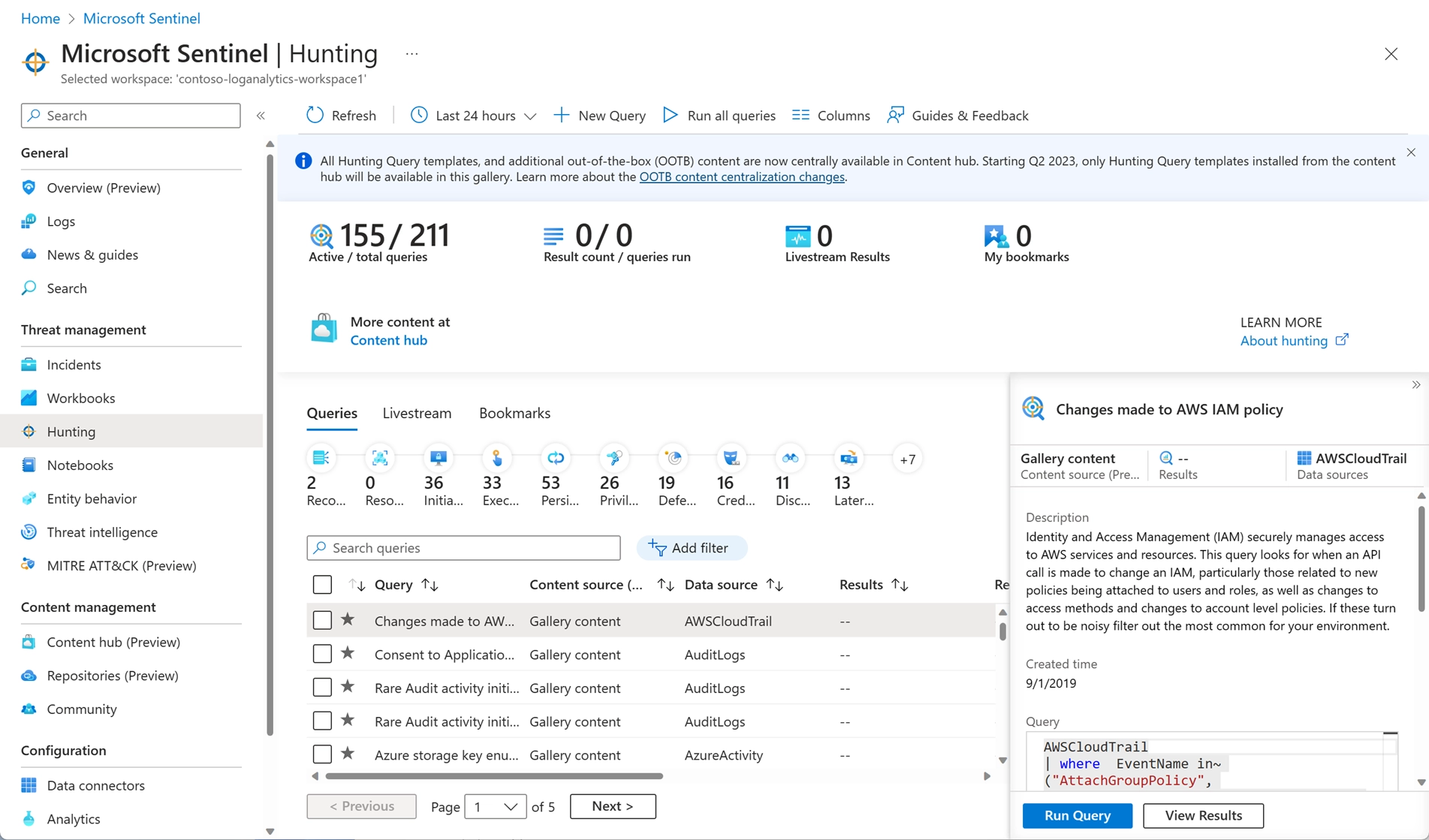
Figure: Threat Hunting in Microsoft Sentinel, Image courtesy of Microsoft Azure
Incidents and investigations in Microsoft Sentinel
In case of possible incidents detected, Microsoft Sentinel can step in and conduct standard incident management tasks like changing status or assigning incidents to individuals for investigation. Since it has investigation functionality, so cloud engineers can now visually investigate incidents by mapping entities across log data along a timeline.
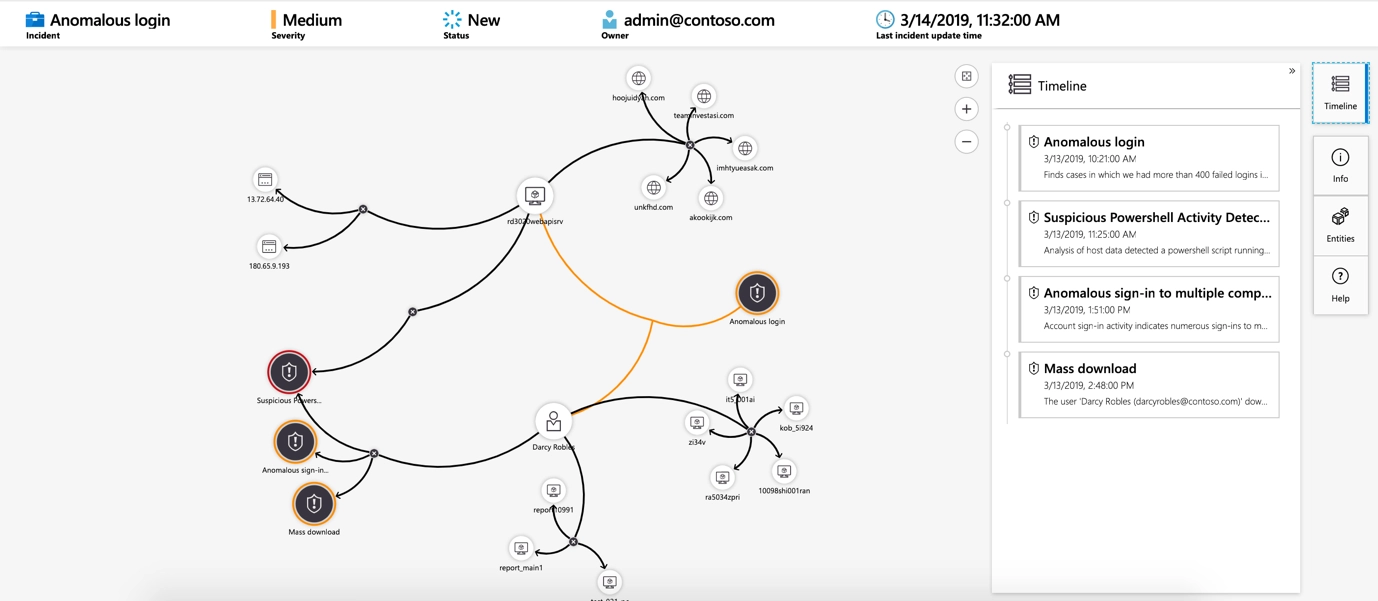
Figure: Incidents Investigation in Microsoft Sentinel, Image courtesy of Microsoft Azure
Automation Playbooks in Microsoft Sentinel
With the capability to automatically respond to incidents, cloud engineers can now streamline security operations and enhance productivity in your Security Operations Center (SOC). This is because Microsoft Sentinel enables you to build automated workflows, known as playbooks, in response to specific events. These playbooks can be utilized for incident management, data enrichment, investigation, or remediation. Collectively, these functionalities fall under the umbrella of security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR).
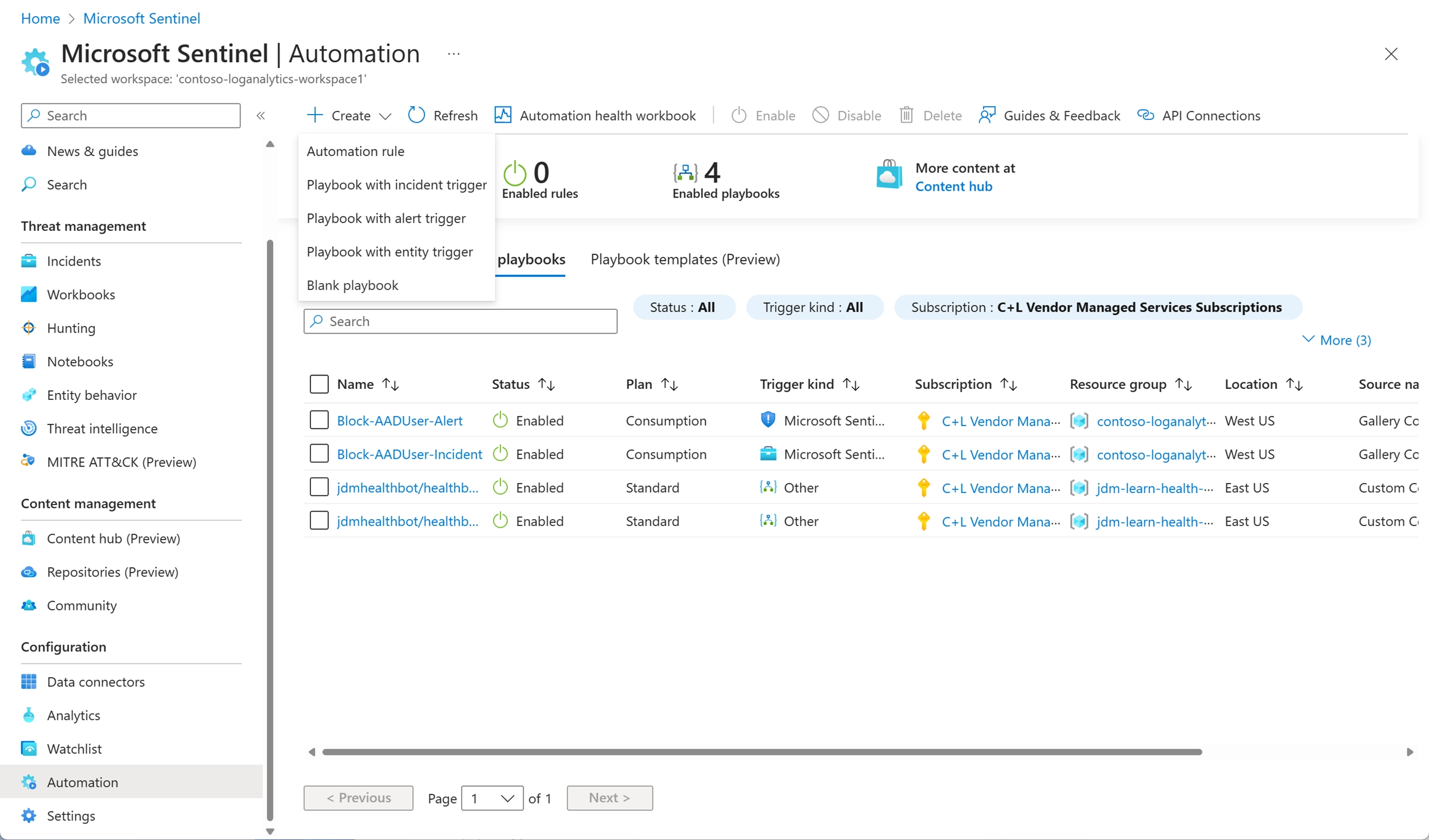
Figure: Automation Playbooks in Microsoft Sentinel, Image courtesy of Microsoft Azure
What capabilities that Microsoft Sentinel can help Cloud Engineers?
Here are some of the ideal situations that Microsoft Sentinel can take care us of in daily end-to-end security solutions.
1. Data Collection at Cloud Scale (Microsoft Sentinel)
Microsoft Sentinel collects data from various sources, including users, applications, servers, and devices running on-premises or in any cloud. This extensive data collection capability ensures that no potential threat goes unnoticed.
Real-World Example:
A global retail company uses Microsoft Sentinel to collect and analyze data from its e-commerce platform, customer databases, and internal systems. This comprehensive data collection helps the company detect and respond to potential security threats, such as unauthorized access attempts and data breaches
2. Advanced Threat Detection (Microsoft Sentinel)
Sentinel uses built-in AI and machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies and potential threats. It correlates data from multiple sources to identify suspicious activities and minimize false positives, ensuring that security teams can focus on genuine threats.
Real-World Example:
A financial institution leverages Sentinel’s advanced threat detection capabilities to monitor transactions and user activities. When Sentinel detects unusual patterns, such as multiple failed login attempts or large, unexpected transfers, it alerts the security team to investigate further.
3. Automated Response (Microsoft Sentinel)
With Sentinel, organizations can automate common security tasks using playbooks. These playbooks, built on Azure Logic Apps, enable automated responses to incidents, reducing the time and effort required to mitigate threats.
Real-World Example:
A healthcare provider uses Sentinel’s automated response capabilities to handle phishing attacks. When Sentinel identifies a phishing email, it automatically triggers a playbook that quarantines the email, notifies the affected user, and initiates a security investigation.
4. Investigation and Hunting (Microsoft Sentinel)
Sentinel provides powerful tools for threat investigation and hunting. Security analysts can use built-in queries and custom KQL (Kusto Query Language) queries to search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) and investigate incidents in-depth.
Real-World Example:
A technology company employs Sentinel’s threat hunting tools to proactively search for signs of compromise in its cloud infrastructure. By regularly running custom queries, the security team can identify and address potential vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
5. Integration with Microsoft Ecosystem
Sentinel integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft services, such as Azure Active Directory, Microsoft 365 Defender, and Azure Monitor. This integration enhances its capabilities, providing a unified view of the security landscape.
Real-World Example:
An educational institution integrates Sentinel with Azure Active Directory to monitor and protect student and faculty accounts. This integration helps the institution detect and respond to suspicious login attempts and potential account compromises.
How Microsoft Sentinel monitor Azure Cloud Systems
1. Real-Time Monitoring (Microsoft Sentinel)
Sentinel offers real-time monitoring of cloud environments, ensuring that any suspicious activity is detected and addressed promptly. It continuously analyzes data from various sources to provide up-to-date security insights.
Real-World Example:
A logistics company uses Sentinel to monitor its cloud-based fleet management system. Real-time monitoring helps the company detect and respond to potential security threats, such as unauthorized access to vehicle tracking data.
2. Threat Intelligence (Microsoft Sentinel)
Sentinel leverages threat intelligence from Microsoft and other sources to stay ahead of emerging threats. This proactive approach helps organizations protect their cloud systems from the latest security risks.
Real-World Example:
A media company subscribes to multiple threat intelligence feeds integrated with Sentinel. This allows the company to stay informed about new threats targeting the media industry and adjust its security measures accordingly.
3. Compliance and Reporting (Microsoft Sentinel)
Sentinel helps organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements by providing detailed audit logs and compliance reports. These reports can be customized to meet specific regulatory standards, ensuring that organizations remain compliant.
Real-World Example:
A financial services firm uses Sentinel to generate compliance reports for regulatory bodies. These reports include detailed logs of security incidents and responses, helping the firm demonstrate its adherence to industry regulations.
How Microsoft Sentinel protect Azure Cloud Systems
1. Automated Incident Response
Sentinel’s automated response capabilities enable organizations to respond to incidents quickly and efficiently. By automating routine tasks, security teams can focus on more complex threats and reduce the overall response time.
Real-World Example:
An online retailer uses Sentinel to automate responses to DDoS attacks. When Sentinel detects a potential DDoS attack, it automatically triggers a playbook that activates additional security measures and notifies the IT team.
2. Threat Hunting
Sentinel provides advanced threat hunting capabilities, allowing security analysts to proactively search for threats. Using custom queries and watchlists, analysts can identify and mitigate potential threats before they cause harm.
Real-World Example:
A government agency employs Sentinel’s threat hunting tools to search for indicators of nation-state attacks. By regularly updating watchlists and running custom queries, the agency can detect and respond to sophisticated threats.
3. Collaboration and Communication
Sentinel integrates with Microsoft Teams, enabling seamless collaboration and communication during incident response. Security teams can manage incident queues, share insights, and coordinate responses in real-time.
Real-World Example:
A multinational corporation uses Sentinel and Microsoft Teams to coordinate its global security operations. During a security incident, teams from different regions can collaborate in real-time, ensuring a swift and coordinated response.
CONCLUSION
Microsoft Sentinel is a powerful tool for cloud security monitoring and protection. Its advanced threat detection, automated response, and seamless integration with the Microsoft ecosystem make it an essential solution for modern organizations. By leveraging Sentinel, organizations can enhance their security posture, protect their cloud systems, and stay ahead of emerging threats.
Whether you’re looking to improve your threat detection capabilities, automate incident response, or ensure regulatory compliance, Microsoft Sentinel offers the tools and features you need to secure your cloud environment effectively.
I hope this detailed blog with real-world examples helps you understand the capabilities and benefits of Microsoft Sentinel for cloud security. If you have any specific questions or need further information, feel free to ask!






